The Alarming Growth of Webpage Sizes: Understanding Causes and Optimization Strategies
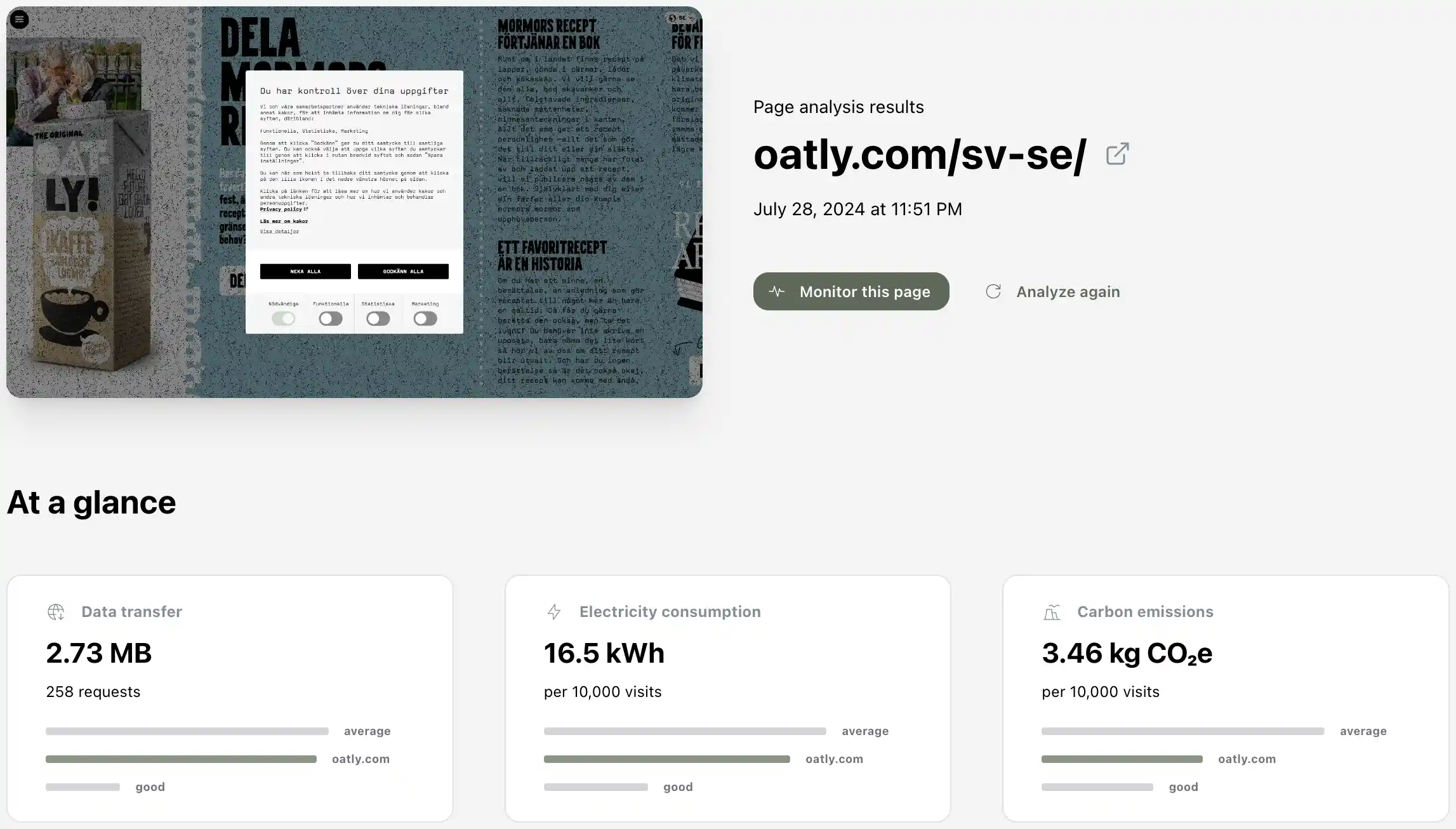
Websites have undergone significant transformation in recent years, with one particularly concerning trend emerging: the exponential growth of webpage sizes. Earlier this year, we took a break from Merely Emissions, a project dedicated to monitoring this issue. However, the problem continues to escalate as companies prioritize feature-rich websites over efficiency, often due to a lack of awareness about the environmental and performance implications. In this article, we'll explore the statistics behind webpage size increases, the factors driving this growth, and the critical importance of optimization. Despite Merely Emissions being paused, this issue remains crucial and deserves our attention.
The Growth of Webpage Size
The average webpage size has increased significantly over the years:
- In 2012, the average webpage size was 803 KB for desktop sites and 386 KB for mobile sites.
- By August 2017, the average webpage size had grown to approximately 1.6 MB for desktop sites.
- As of September 2022, the average webpage size reached about 2.2 MB for desktop sites and 2 MB for mobile sites.
This represents a staggering increase of 184% for desktop sites and 420% for mobile sites over the past decade. The trend continues, with reports indicating that as of July 2023, the average webpage size for top sites worldwide is around 2484 KB.
Key Contributors to Increased Webpage Size
Several factors contribute to the growing size of webpages:
Images
Images are the most significant contributors to webpage size. In 2017, images accounted for an average of 1,818 KB per page. As websites increasingly rely on high-quality visuals to engage users, the size of images continues to rise.
JavaScript
JavaScript plays a crucial role in creating dynamic and interactive user experiences. The average script size for desktop sites in 2022 was 316 KB, marking a substantial increase of 350 KB compared to 2012. This growth is mainly due to the adoption of complex frameworks and libraries.
Videos
Videos have become a staple of online content, enhancing storytelling and engagement. While they accounted for only 7.7% of total page size in 2016, they added an average of 174 KB more than in 2010. As video content becomes more prevalent, it significantly impacts overall webpage size.
Fonts
Custom fonts have gained popularity in web design, contributing to the aesthetic appeal of websites. As of September 2022, fonts accounted for approximately 143 KB on desktop and 124 KB on mobile devices.
The Importance of Optimization
While the growth in webpage size reflects advancements in web design, it also raises concerns about loading times and user experience. Larger pages can lead to slower load times, frustrating users, and resulting in higher bounce rates.
To mitigate these issues, web developers and site owners should prioritize optimization strategies, including:
- Image Compression: Reduce the file size of images without sacrificing quality.
- Minifying Code: Remove unnecessary characters from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files to decrease load times.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and videos to ensure that only the necessary content is loaded initially.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs are used to distribute content more efficiently and reduce server load.
Conclusion: Advocating for Sustainable Web Practices
The dramatic increase in webpage size over the past decade reflects advancements in web design but also poses significant challenges to performance and environmental sustainability. As we embrace more sophisticated web technologies, it's crucial for developers and tech companies to prioritize optimization strategies.
While Merely Emissions is currently inactive, the importance of addressing webpage bloat has only grown. By raising awareness about the environmental impact of large webpages, we can encourage companies to create more efficient digital experiences. Even without an active project, each of us can advocate for sustainable web practices and urge tech companies to lead in building a more efficient internet for all. These revisions ensure consistency between the introduction and conclusion, properly frame the current status of Merely Emissions, and introduce readers to the content of the article.
No spam, no sharing to third party. Only you and me.


